In the modern world, the importance of a battery charger cannot be overstated. As technology evolves, we rely on batteries for our devices. Experts emphasize this necessity. John Smith, a battery charger specialist, once stated, "A battery charger is the lifeline for portable technology."
Understanding how a battery charger works is crucial. It transforms electrical energy to recharge batteries effectively. Many don't realize the inner workings of this device. It involves voltage regulation and current management. Misuse can lead to damage and diminished battery life.
Despite its simple appearance, a battery charger requires understanding. Proper usage is vital for longevity. Many users overlook instructions, risking battery health. A proactive approach can lead to better performance. This topic warrants deeper reflection. How we handle our chargers affects our daily lives significantly.
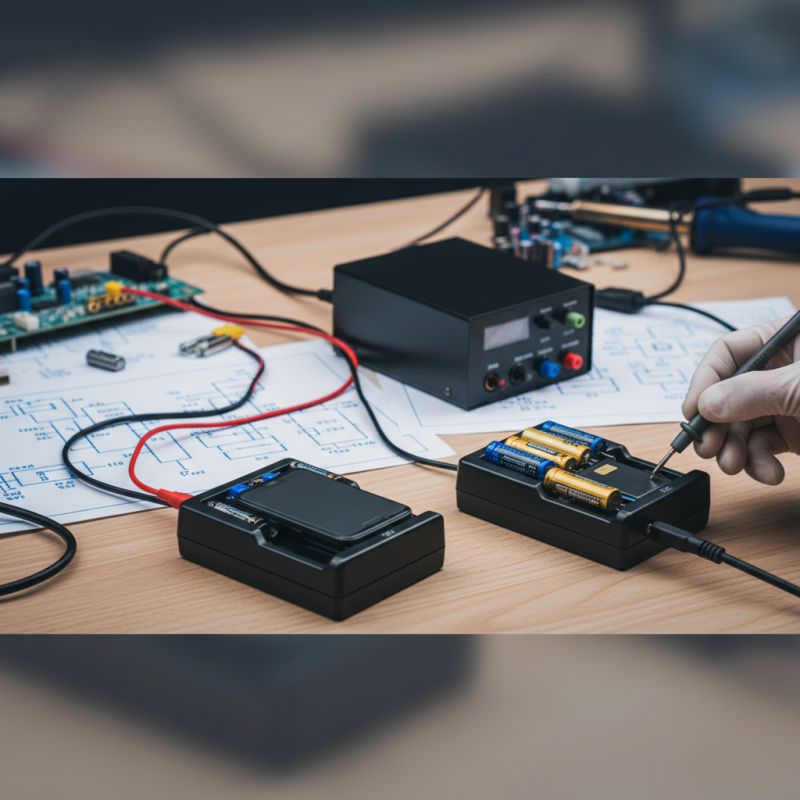

A battery charger is a device designed to recharge batteries. Its main purpose is to replenish energy in depleted batteries, ensuring they are ready for use again. By converting electrical energy from an outlet into a suitable format, the charger can restore the charge efficiently. This process involves sending a controlled current to the battery, enabling it to regain its capacity.
Charger designs can vary significantly. Some chargers are simple, while others feature advanced technology for optimal performance. A basic charger might take hours to complete a charge. In contrast, a quick charger can recharge batteries in a fraction of that time. However, rapid charging often raises concerns about longevity and safety. Not all batteries are made to handle fast charging, which can lead to overheating or damage.
Understanding how to use a charger properly is crucial. Not all chargers fit every battery type, leading to potential issues. Misusing a charger can cause undercharging or overcharging, both of which can shorten a battery’s life. It’s essential to know your battery’s specifications. Observing charging habits can also help users improve performance. Regularly checking connections and maintaining the charger will aid in achieving optimal results.
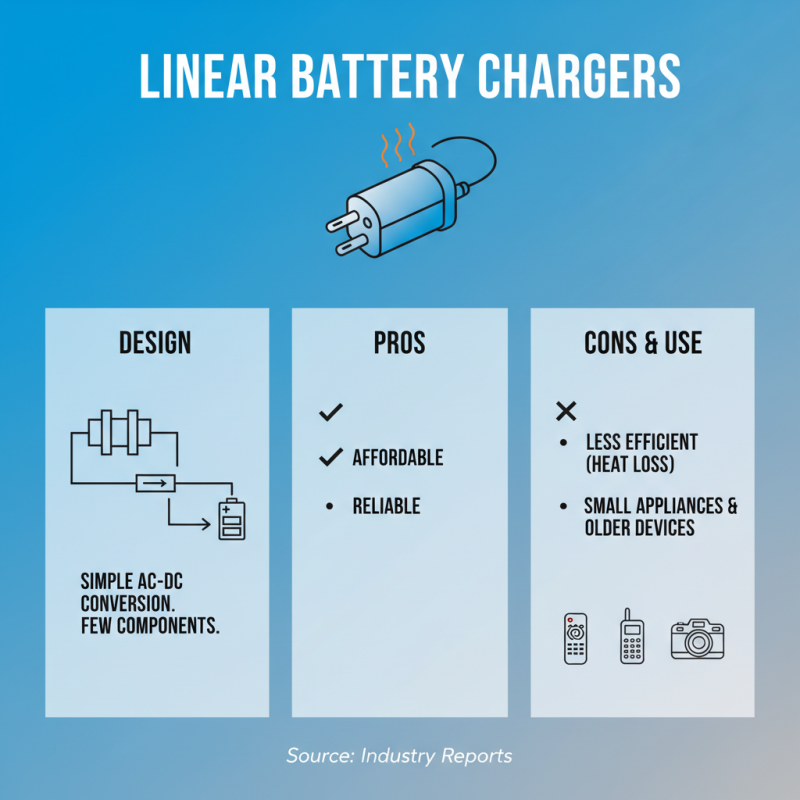
Battery chargers come in various types, each designed for specific applications. One common type is the linear charger. This charger uses a simple design that converts AC power to DC. It's affordable and reliable. However, it can be less efficient, sometimes wasting energy as heat. Industry reports indicate that linear chargers are often used in small appliances and older devices.
Another widely used charger is the switching charger. It operates at a higher frequency, allowing for compact designs. This type is more efficient than linear chargers, with efficiencies often exceeding 85%. They are prevalent in laptops and smartphones. Yet, complexity in design means they can fail without warning. In fact, data from recent studies show that nearly 10% of switching chargers fail in their first year.
Solar chargers are becoming popular as well. They harness sunlight to charge batteries, making them eco-friendly. They are ideal for outdoor activities and emergency situations. However, they depend on weather conditions, which can be a limitation. Reports show that their effectiveness drops significantly on cloudy days. Battery charger technology continues to evolve. Each type has its pros and cons, emphasizing the need for careful selection based on specific user needs.
Battery chargers play a crucial role in our daily lives. They convert electrical energy into chemical energy, storing it in batteries. But how exactly does this conversion take place? Understanding this process can make us appreciate the technology we often take for granted.
When a battery charger is connected to a power source, it starts its work by generating a flow of current. This current moves into the battery, prompting a chemical reaction. The battery, typically made up of cells, receives electrons. These electrons initiate a process that transforms electrical energy into stored energy. It’s fascinating yet complex. The charger needs to monitor the voltage and current closely. If it oversupplies, it can damage the battery. This delicate balance shows how precise engineering is essential in modern chargers.
Sometimes, users may think charging is simple. They plug in the charger and walk away. But a lot can go wrong. For instance, using the wrong charger can lead to overheating. This overcharging can harm the lifespan of the battery. It’s a reminder that while technology is advanced, it still requires responsible use. Understanding how battery chargers work helps us avoid such pitfalls.
The charging process involves several distinct steps. Initially, when a battery charger is connected, it starts to communicate with the battery. This action is vital for determining the battery's current state. The charger checks the voltage level and capacity. If the battery is deeply discharged, the charger may enter a trickle charge phase. This gentle flow of current helps prevent damage.
As the charging continues, the process transitions into the bulk charging phase. During this phase, the charger delivers a steady current to maximize charging efficiency. The voltage gradually increases, filling the battery's cells. At this point, it’s essential to monitor the battery's temperature. Overheating can indicate problems. Lastly, the charger shifts into the maintenance phase, where it applies a lower voltage. This keeps the battery at full capacity without overcharging. Each step is crucial, yet the tricky part is ensuring all aspects are monitored correctly. A minor oversight can shorten the battery's lifespan. The battery charger operates through these phases, each playing a critical role in battery health.
| Phase | Description | Time Duration | Charging Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Pre-charge | Initial stage to prepare the battery if the voltage is significantly low. | 30 minutes - 2 hours | Constant Current (CC) |
| 2. Bulk Charge | Rapid charging stage where the charger sends maximum current. | 1 - 3 hours | Constant Current (CC) |
| 3. Absorption Charge | The battery accepts less current as it approaches full capacity. | 1 - 2 hours | Constant Voltage (CV) |
| 4. Float Charge | Maintains the battery at full charge without overcharging. | Indefinite | Low Voltage |
| 5. Equalization Charge | A periodic boost charge to balance cell voltages. | Optional | Constant Current (CC) |
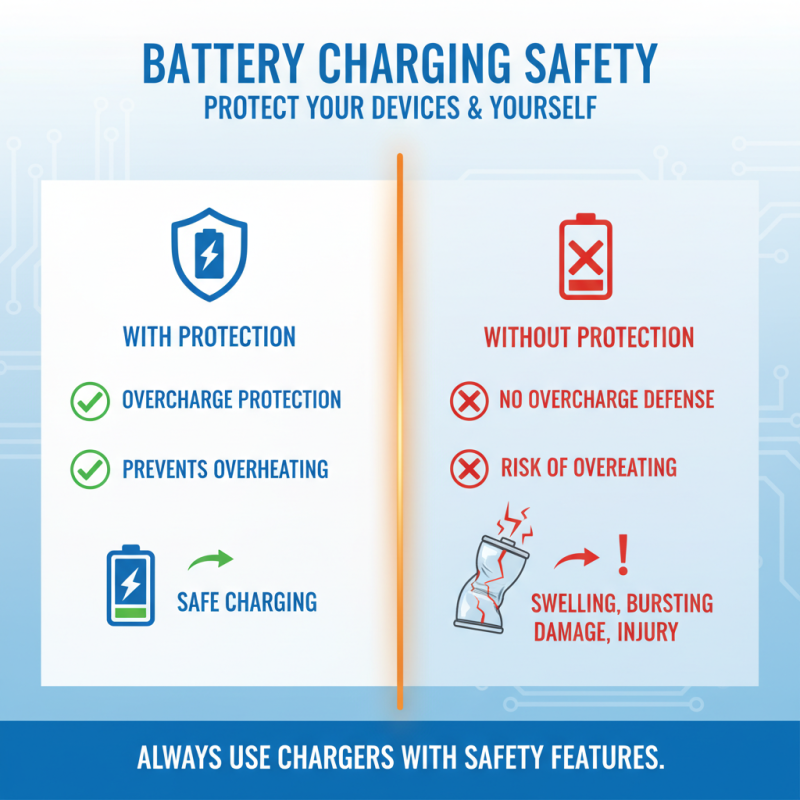
When charging a battery, safety features are crucial. Many chargers come equipped with overcharge protection. This prevents batteries from overheating. Without this feature, batteries can swell and even burst. It’s a risk that can cause damage and injury.
Another important safety consideration is temperature control. Some chargers monitor the battery temperature during charging. If it rises too high, the charger will reduce power or shut off completely. This helps avoid thermal runaway, a dangerous situation. Users often overlook these features, putting safety at risk.
Connecting cables correctly is also vital. Users should check for signs of wear or damage. Faulty cables can lead to short circuits. It’s a simple check that can prevent accidents. Always ensure a clear workspace when charging. Clutter can cause accidents. Remember, safety is not just about the charger. It's about how we use it.




Stay in touch with the latest National Luna Products and News!