The fridge freezer is an essential appliance in modern households, playing a crucial role in food preservation and storage. According to recent market research, the global fridge freezer market was valued at approximately $120 billion in 2022, with projections indicating steady growth as consumers seek energy-efficient and space-saving solutions. As the trend towards compact living continues, incorporating a fridge freezer into home design not only enhances convenience but also aligns with contemporary lifestyle demands.
These versatile appliances combine refrigeration and freezing capabilities, allowing users to store a diverse range of food items at optimal temperatures. Industry experts highlight that utilizing a fridge freezer effectively can reduce food wastage by up to 30%, significantly benefiting both household budgets and environmental sustainability. As innovation drives the development of smart fridge freezers equipped with advanced features such as temperature control and connectivity, homeowners are presented with an opportunity to elevate their kitchen experience while ensuring food safety and freshness.
Understanding how a fridge freezer operates is vital for making informed choices in home appliances. This knowledge can lead to improved energy efficiency and cost savings over time, ultimately enhancing the quality of life for families around the globe. As we delve deeper into the workings of fridge freezers, it becomes evident that they are more than just appliances; they are essential partners in maintaining a healthy and organized home.
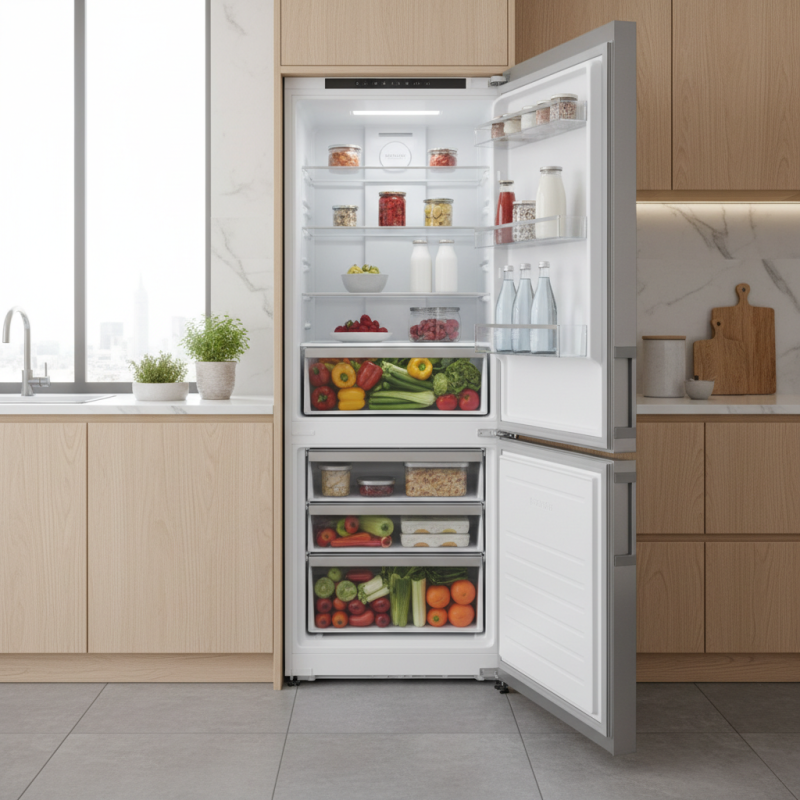


A fridge freezer, an essential appliance in modern households, combines a refrigerator and freezer into one unit, offering convenience and efficient food storage. The main components of a fridge freezer include the compressor, evaporator, condenser, and thermostat. The compressor acts as the heart of the system, circulating refrigerant throughout the unit. As the refrigerant evaporates in the evaporator coils, it absorbs heat from the interior, facilitating the cooling process. The condenser then releases this heat outside, maintaining the desired temperature inside the fridge and freezer compartments.
An interesting aspect of fridge freezers is their energy efficiency. According to the U.S. Department of Energy, Energy Star-rated appliances can save homeowners up to 10-50% on energy bills compared to non-rated models. This not only benefits your wallet but also contributes to environmental sustainability. Many modern fridge freezers come equipped with features such as LED lighting and smart thermostats that adjust energy usage based on the contents and usage patterns.
**Tips:** Regular maintenance can keep your fridge freezer running optimally. Ensure that the door seals are airtight to prevent warm air from entering, leading to energy wastage. Additionally, setting your fridge temperature between 35°F and 38°F (1.6°C to 3.3°C) and your freezer at 0°F (-18°C) maximizes food preservation while minimizing energy consumption. Clean the condenser coils every six months to enhance efficiency and longevity.
A fridge freezer is an essential appliance in modern homes, seamlessly combining refrigeration and freezing functions in a single unit. This innovative design not only maximizes space efficiency but also optimizes food preservation. According to industry data, about 70% of households utilize fridge freezers, underscoring their importance for maintaining food safety and reducing waste. The refrigeration component operates at temperatures usually ranging from 32°F to 40°F, inhibiting bacterial growth and keeping perishable items fresh. In contrast, the freezing compartment operates at temperatures below 32°F, locking in nutrients and flavors for longer storage.
When selecting a fridge freezer, efficiency is key. Look for models with high Energy Star ratings, which can lead to savings of up to 30% on energy costs compared to standard models. Frequent maintenance, such as cleaning condenser coils and ensuring door seals are intact, can also improve energy efficiency and prolong the appliance's lifespan.
Tips: Consider organizing your fridge freezer with clear bins and labels to maximize space and minimize food spoilage. Additionally, keep an inventory of what you have stored, making it easier to plan meals and avoid over-purchasing. Regularly check items and use a first-in, first-out method to ensure older food is consumed before newer items.
The operation of a fridge freezer is rooted in fundamental principles of physics, primarily involving heat transfer and thermodynamics. At its core, the appliance uses a refrigeration cycle, which leverages the physical properties of refrigerants—substances that absorb and release heat efficiently. The cycle begins in the compressor, where the refrigerant gas is compressed, increasing its pressure and temperature. This hot gas then moves through the condenser coils, where it releases heat to the surrounding environment and transforms into a liquid state.
Once in liquid form, the refrigerant passes through an expansion valve, causing a rapid decrease in pressure, which cools it down significantly. This cold refrigerant then enters the evaporator coils inside the fridge and freezer compartments. Here, it absorbs heat from the interior, effectively cooling the air within. As the refrigerant absorbs heat, it evaporates back into gas, and the cycle repeats. Temperature control in fridge freezers is achieved through thermostats that regulate the compressor's activity, ensuring the interior environments remain at optimal levels for preserving food.
The efficiency of this process is influenced by various factors, including environmental temperature and appliance design. Insulation plays a critical role as it minimizes heat exchange with the external environment, allowing the fridge freezer to maintain consistent temperatures without excessive energy consumption. Additionally, the strategic placement of fans helps in circulating air evenly within the compartments, preventing temperature fluctuations and enhancing the overall cooling efficiency.
The chart above illustrates the optimal and maximum temperature settings for both fridge and freezer compartments, ensuring food safety and preservation.

A fridge freezer is an essential appliance in modern homes, combining refrigeration and freezing in a single unit. One of the primary benefits of using a fridge freezer is energy efficiency. According to the U.S. Department of Energy, newer fridge freezer models can use up to 50% less energy than older units, contributing to lower electricity bills and a reduced carbon footprint. This efficiency is particularly important as households aim to minimize environmental impact while maintaining their food preservation needs.
Another significant advantage is the convenience it offers. A fridge freezer allows for optimal food storage by enabling users to freeze perishables, extending their shelf life significantly. For instance, the average family can waste up to $1500 a year on food that spoils before it is consumed, as reported by the USDA. The combination of freezing and refrigeration in one appliance not only saves space but also makes meal preparation more streamlined. Families can buy in bulk and freeze items, leading to reduced shopping frequency and better management of food supplies. In this way, fridge freezers contribute not just to savings but also to a more organized kitchen environment.
To maintain optimal performance of your fridge freezer, regular cleaning and organization are essential. Start by decluttering the interior; remove expired items and wipe down shelves with a mild detergent. A clean fridge not only looks better but also helps in maintaining airflow, which is crucial for temperature consistency. Organizing food items by type and usage can enhance efficiency, making it easier to find what you need and minimizing door openings, which can raise internal temperatures.
Another key aspect of maintaining your fridge freezer is monitoring its temperature settings. Ideally, the fridge should be set between 35°F and 38°F (1.7°C to 3.3°C) while the freezer should remain at 0°F (-18°C). Periodically check these settings using a thermometer, as improper temperatures can compromise food safety and speed up spoilage.
Additionally, ensure the seals around the doors are intact; testing them by closing a piece of paper in the door can show if there’s a proper seal. If the paper easily slips out, it's time to replace the seals to prevent cold air from escaping, ultimately improving energy efficiency.





Stay in touch with the latest National Luna Products and News!